The selection and design of any biomass combustion system are determined mainly by the characteristics of the fuel to be used, existing environmental legislation, the costs and performance of the equipment available, as well as the energy and capacity needed (heat, electricity).
Due to economy of scale effects concerning the fuel feeding system, the combustion technology, and the flue gas cleaning system, usually large-scale systems use low-quality fuels, while high-quality fuels are typically used for small-scale systems. Therefore, large-scale biomass combustion technologies are often similar to waste combustion systems, but when clean biomass fuels are utilised, the flue gas cleaning technologies are less complex and therefore cheaper. Improvements are continuously being made in fuel preparation, combustion and flue gas cleaning technologies. This leads to significant improvements in efficiencies, and reductions in emissions and costs, as well as improved fuel flexibility and plant availability, and opens new opportunities for biomass combustion applications under conditions that were too expensive or inadequate before.
For any biomass combustion application, emission reduction and efficiency improvement are major goals. The results of research projects and experiences of demonstration plants in one country can have a strong impact on other countries as well, and here the IEA collaboration plays an important role in information exchange.
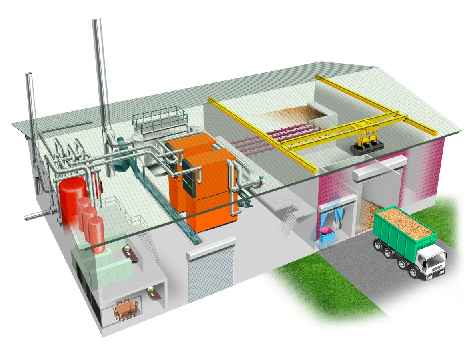 |
| Lay-out of the Wilderswil heating plant (6,4 MWth on wood chips + 3 MWth backup on fuel oil). Courtesy of Schmid AG, Switzerland. |


